Pelvic pain
Menstrual bleeding usually occurs each 28 days. Sometimes the cycle may be longer or shorter than 28 days. At times the cycle may be very irregular, or bleeding may become very heavy. This may just be due to a temporary hormonal imbalance, but it can be due to problems in the uterus or the ovaries.
Endometrial polyps
A small growth of the tissue of the lining of the uterus (endometrial polyp) can occur. These can cause periods to be heavier or to have bleeding at unusual times. Mostly these are not cancerous, but occasionally if left alone for a long time they can become cancerous. Polyps can usually be seen on transvaginal ultrasound, but a technique called sonohysterography can be used to make them easier to see.
Septate Uterus
Fibroids are a growth arising from the muscle of the uterus. They can press on the lining of the uterus (endometrium) and cause irregular bleeding or heavy periods. It is very rare for a fibroid to become cancerous.
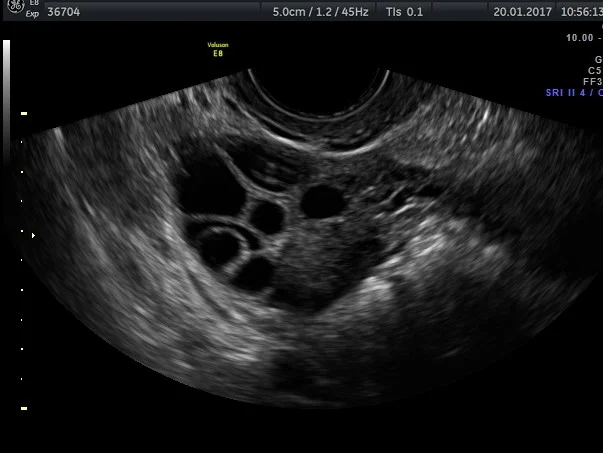
Polycystic ovarian
The ovaries produce hormones which control the uterus. Some conditions can alter the hormonal production and stop the ovaries producing an egg (ovulation) each month. An example of this is polycystic ovarian syndrome
During the reproductive years, the ovaries are continually going through the cycle of egg production. This involves the formation and resolution of a cyst. Sometimes this process does not function perfectly and the cyst may become very large.
Ovarian cancer can also produce a mass. Ultrasound can help to find it at an early stage, when treatment may be able to get a good long term result.
Pelvic pain
Pain can be caused by any organ in the abdomen and it may be difficult without tests like ultrasound to establish the exact cause. Because ultrasound can distinguish between many of the diagnostic possibilities non-invasively, it is the preferred initial imaging technique.
Discomfort with the onset of a period is common. Sometimes a problem like endometriosis can cause severe pain and cysts can be seen. These cysts are often on or near the ovary.
The ovaries produce a cyst each month. These usually resolve around the time of the next period, but sometimes they can become larger and tender.
The bowel can cause pain which can be in different positions at different times. It is usually a dull crampy pain and can be related to diet and stress
Pelvic scan
Gynaecology refers specifically to the study and treatment of pelvic disorders in women.
Ultrasound is a very efficient and safe imaging modality with which to examine the female pelvic organs.
Gynacological ultrasound examinations usually involve both an abdominal and vaginal scan.
Transabdominal scan: An ultrasound probe is placed on the abdomen and by utilizing the “window”produced by a full bladder the uterus and ovaries can most often be seen as well as any large pelvic masses or free fluid.
Transvaginal scan: With an empty bladder, a small ultrasound probe covered by a disposable protective sheath is gently inserted into the vagina, either by the patient or the sonographer. This method of scanning allows for a better quality image of the uterus, cervix, fallopian tubes and ovaries.
While our medical preference is for the higher quality images that the transvaginal scan provides it is only performed with the patient’s consent and comfort in mind.